CfnCluster Auto Scaling¶
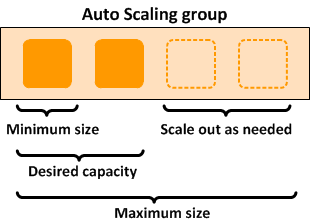
Clusters deployed with CfnCluster are elastic in several ways. The first is by
simply setting the initial_queue_size and max_queue_size parameters of a cluster
settings. The initial_queue_size sets minimum size value of the ComputeFleet
Auto Scaling Group (ASG) and also the desired capacity value . The max_queue_size
sets maximum size value of the ComputeFleet ASG.
Scaling Up¶
Every minute, a process called jobwatcher runs on the master instance and evaluates
the current number of instances requested in the queue. If this number is greater than the
current autoscaling desired, it adds more instances. If you submit more jobs,
the queue will get re-evaluated and the ASG updated up to the max_queue_size.
Scaling Down¶
On each compute node, a process called nodewatcher runs and evaluates the
work left in the queue. If an instance has had no jobs for longer than scaledown_idletime
(which defaults to 10 minutes), the instance is terminated.
It specifically calls the TerminateInstanceInAutoScalingGroup API call, which will remove an instance as long as the size of the ASG is at least the minimum ASG size. That handles scale down of the cluster, without affecting running jobs and also enables an elastic cluster with a fixed base number of instances.
Static Cluster¶
The value of the auto scaling is the same for HPC as with any other workloads,
the only difference here is CfnCluster has code to specifically make it interact
in a more intelligent manner. If a static cluster is required, this can be
achieved by setting initial_queue_size and max_queue_size parameters to the size
of cluster required and also setting the maintain_initial_size parameter to
true. This will cause the ComputeFleet ASG to have the same value for minimum,
maximum and desired capacity.
